Choosing the right caster load capacity is vital for maintaining both safety and functionality in your equipment. In this guide, I’ll show you how to calculate the load capacity for caster wheels, ensuring you make the right choice for your needs.
Steps to Calculate Caster Load Capacity
The 4 steps to calculate caster load capacity is Determine the total weight, decide the number of casters, calculate minimum load per caster, and apply a safety margin.
Here’s a breakdown of the steps you need to follow to calculate the correct caster load capacity for your project.
🚀 Step 1.Determine the Total Weight
Add together the weight of the load and the equipment (cart, platform, etc.).
Formula 1️⃣:
Total Weight=Weight of Load+Weight of Equipment
🚀 Step 2.Decide on the Number of Casters
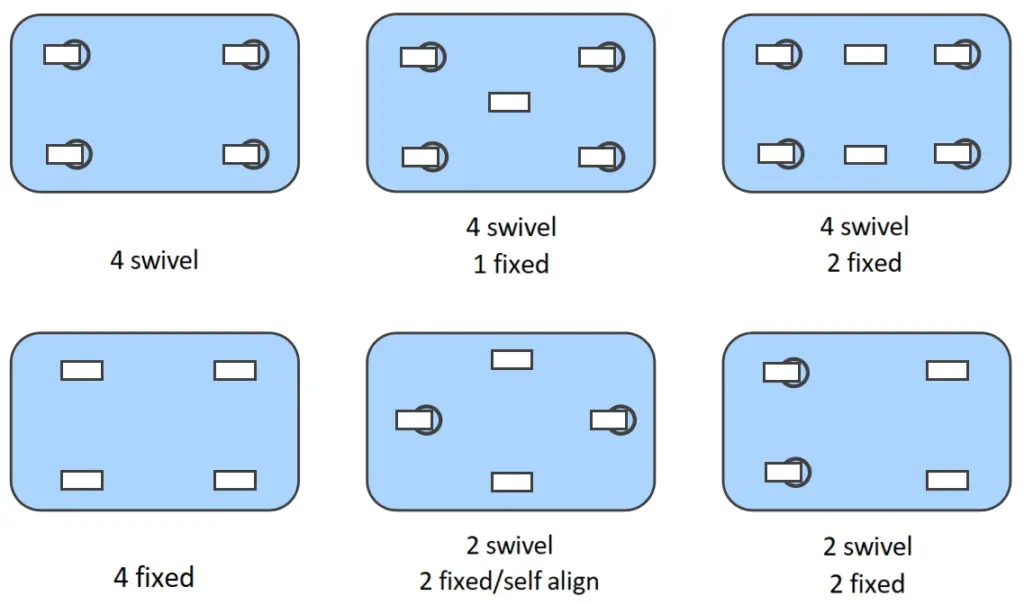
The number of casters needed depends on your equipment’s design. A four-caster setup is common for carts, but other configurations are possible based on the design or load distribution.
🚀 Step 3.Calculate Minimum Load Per Caster
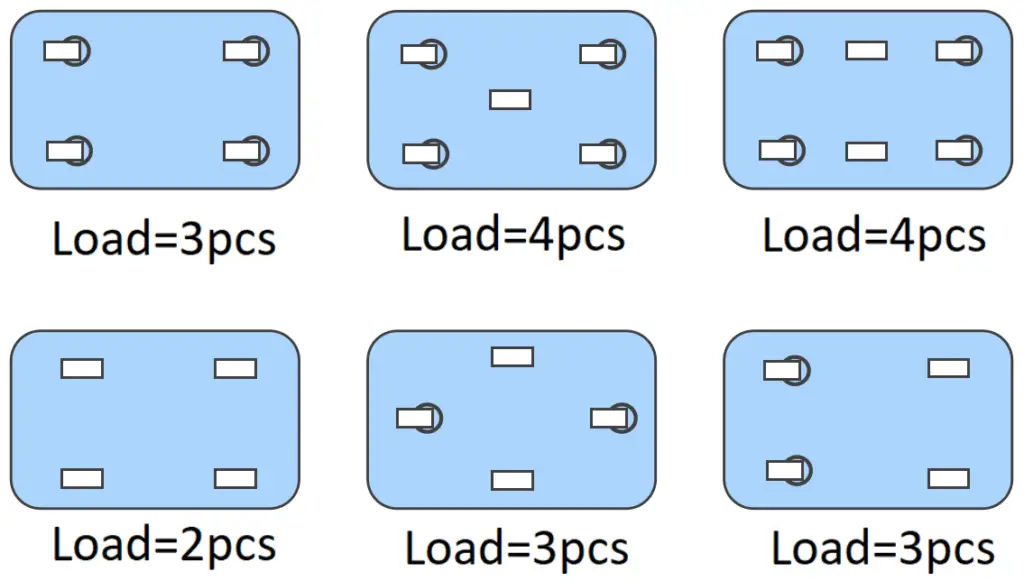
Divide the total weight by the number of casters. However, it’s advisable to account for uneven surfaces by subtracting one or two from the total number of casters.
Formula 2️⃣:
Minimum Load Capacity per Caster=Total Weight/Number of Casters-1 or 2
🚀 Step 4.Apply a Safety Margin
To compensate for dynamic forces and potential overloads, it’s wise to apply a safety factor.
“Safety Factor” is an additional weight allowance added to the calculated load per caster to ensure that the casters can handle unexpected or temporary overloads, variations in load distribution, and wear & tear over time.
It typically ranges from 1.0 to 3.0, although the specific value can vary depending on the application and industry standards. A common safety factor is 1.33 (or 33%).
Formula 1️⃣➕2️⃣:
Adjusted Load Capacity per Caster=Minimum Load Capacity per Caster×1.33
👍 Additional tips:
Safety factor: 1.0 to 1.5, for indoor manual transport, when the height of the obstacles is smaller than 5 % of the wheel diameter;
Safety factor: 1.5 to 2.2, for Outdoor manual transport, when the height of the obstacles is bigger than 5 % of the wheel diameter;
Safety factor: 1.4 to 2.0, for indoor power-driven transport, when the height of the obstacles is smaller than 5 % of the wheel diameter;
Safety factor: 2.0 to 3.0, for outdoor power-driven transport.
Example Calculation
Let’s walk through an example to clarify the process:
Scenario:
You have a cart that weighs 100 lbs and will carry a load of 2000 lbs. The total weight would be:
Total Weight=2000lbs(kgs)+100lbs(kgs)=2100lbs(kgs)
For four casters, we calculate the minimum load capacity per caster as:
Minimum Load Capacity per Caster=2100lbs(kgs)/(4−1)=2100lbs(kgs)/3=700lbs(kgs)
Next, apply the safety factor:
Adjusted Load Capacity per Caster=700lbs(kgs)×1.33=931lbs(kgs)
So, each caster should have a minimum load capacity of 931 lbs(kgs) to ensure it can handle the cart and its load safely.
Want to know exactly how much weight your casters can handle? Our free Caster Load Calculator does the heavy lifting for you. Just plug in your numbers and boom – instant results. No more guesswork. Try it now. 👇
What Is Caster Load Capacity?
Caster load capacity refers to the maximum weight a caster wheel can support without risk of damage or failure. It is crucial to know this number when selecting casters for carts, equipment, or machinery, as it helps ensure smooth, safe operations.
Why Accurate Load Capacity Matters
An incorrect load capacity can lead to caster failure, causing damage to your equipment or posing safety risks. Underestimating the required load capacity could result in caster wheels buckling under pressure, while overloading could cause instability or wear out your casters prematurely. By determining the right load capacity, you help protect your investment in equipment and ensure smoother, safer operations.
Why Is a Safety Margin Necessary?
A safety buffer accounts for unexpected weight shifts, vibrations, and the extra forces generated during movement. A safety factor of 1.33 ensures that even in less-than-ideal conditions, your casters will continue to perform safely and effectively.
Key Factors Affecting Caster Load Capacity
Wheel Characteristics
The size and material of the caster wheel play a significant role in its ability to carry weight. Generally, larger wheels are better equipped to handle heavy loads and provide better maneuverability, especially over rough surfaces.
Other Considerations
When selecting casters, be mindful of the following factors:
- Surface Type: Casters rolling on uneven or rough surfaces experience more wear and may require higher load capacities.
- Wheel Material: Different materials (steel, polyurethane, nylon) have varying load-bearing abilities. Harder materials typically support heavier loads.
Choosing the Right Casters for Your Project
- Evaluate Weight Requirements: Accurately calculate the total weight of your load, including the equipment’s weight. Factor in a safety buffer to ensure durability and performance.
- Assess the Surface Conditions: Smooth surfaces allow for a wider range of caster materials, while rough or uneven floors may require specific treads and larger wheel diameters for optimal performance.
- Choose Materials Wisely:
- For Heavy Loads: Steel or forged steel wheels are best suited for industrial applications.
- For Floor Protection: Polyurethane wheels balance load capacity with reduced wear on surfaces.
- Consider Environmental Factors: If your environment involves exposure to extreme temperatures, moisture, or chemicals, select materials resistant to such conditions, like nylon or stainless steel components.
- Prioritize Maneuverability: Select casters with a tread profile that suits your application. For example, crowned treads improve steering ease, while flat treads enhance weight distribution.
- Account for Braking Needs: If your equipment operates on inclined surfaces or requires frequent stops, consider casters with integrated brakes or locks for added safety.
Key Takeaways
- Always calculate load capacity based on total weight and a safety buffer.
- Consider environmental and surface factors when choosing caster materials and designs.
- Consult us for complex applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, calculating caster load capacity is crucial for ensuring safety, longevity, and optimal performance of your equipment. By following the steps outlined in this guide and considering key factors such as caster material and surface type, you’ll be able to select the right casters for any application, keeping both safety and efficiency top of mind.
FAQS
-
Q: What is the importance of caster wheel diameter in determining load capacity?
A: Larger diameters distribute weight more effectively and improve mobility, especially on uneven surfaces.
-
Q: How is overall load rating calculated for industrial casters?
A: The formula is: u003cstrongu003eLoad Capacity per Caster × (Number of Casters – 1)u003c/strongu003e to account for uneven ground.
-
Q: Why should I add a safety factor to load capacity calculations?
A: A safety factor ensures that the casters can handle dynamic forces, uneven weight distribution, and minor overloads.
-
Q: What materials are best for high-capacity caster wheels?
A: Steel or forged steel wheels are ideal for heavy loads, while polyurethane and TPR wheels offer durability with floor protection.
-
Q: How do heavy-duty casters improve movement for large loads?
A: Heavy-duty casters reduce rolling resistance, making it easier to move large loads with less effort.