Ball bearings are essential components in caster wheels, reducing friction and enabling smooth, efficient movement under heavy loads. This guide explores the ball bearing sizes, code numbers, and model decoding to provide a deeper understanding of commonly used ball bearings in caster wheels.
What Are Ball Bearings and Why Are They Important in Caster Wheels?

Ball bearings are precision-engineered components designed to reduce friction and enhance motion efficiency between moving parts. It consist of an inner ring, outer ring, balls, and a cage that work together to handle loads and ensure durability.
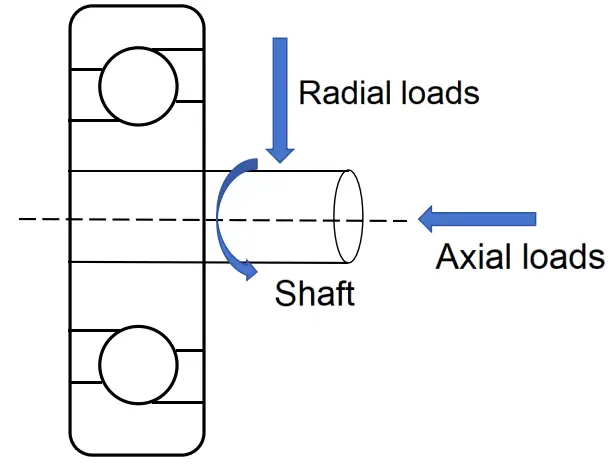
The importance of ball bearings in caster wheels lies in their ability to handle both radial and axial loads, improve durability, and optimize performance.
Key Ball Bearing Terminology Explained
Understanding ball bearing terminology is essential for selecting the right component for caster wheels. Below are the key terms you need to know:
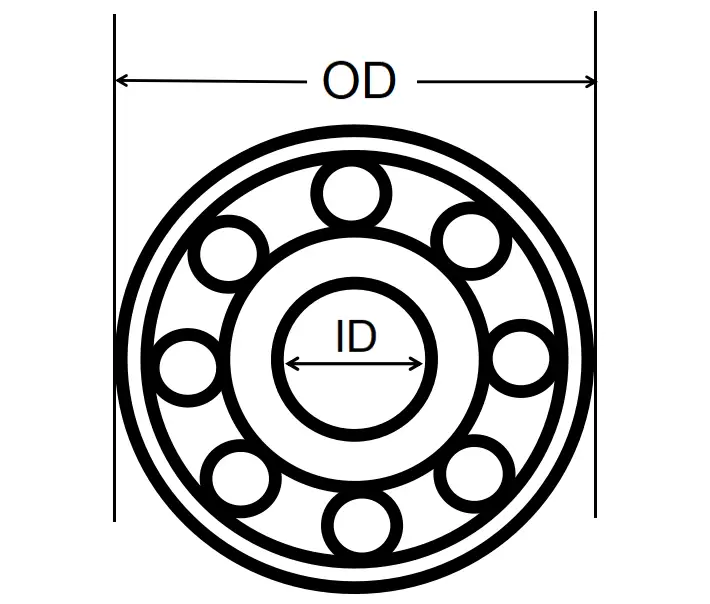
Inner Diameter (ID) and Outer Diameter (OD):
These refer to the dimensions of the bearing. The ID is the size of the hole in the center where the shaft or axle fits, while the OD is the overall width of the bearing’s outer surface.
Width (W):
The width is the measurement of the bearing’s cross-section from one face to the other. This affects the bearing’s load capacity and how it fits into the caster wheel assembly.

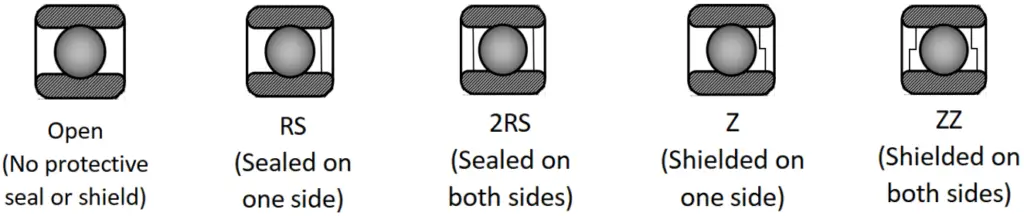
Seal Types:
Bearings can be open, sealed, or shielded, depending on the application.
- Open Bearings: No protective seal or shield, used in clean, controlled environments.
- Sealed Bearings (e.g., 2RS): Offer protection from contaminants like dust and moisture, ideal for harsh environments.
- Shielded Bearings (e.g., ZZ): Protect against larger particles while allowing some airflow, suitable for moderate conditions.
Clearance
In certain cases, a bearing may include an additional suffix, such as C3, which is typically marked on the bearing’s outer diameter (except for CN, which is often unmarked). This suffix indicates the bearing’s clearance code, referring to the internal clearance or the space between the bearing’s components. Refer to the table below for examples and their corresponding clearances.
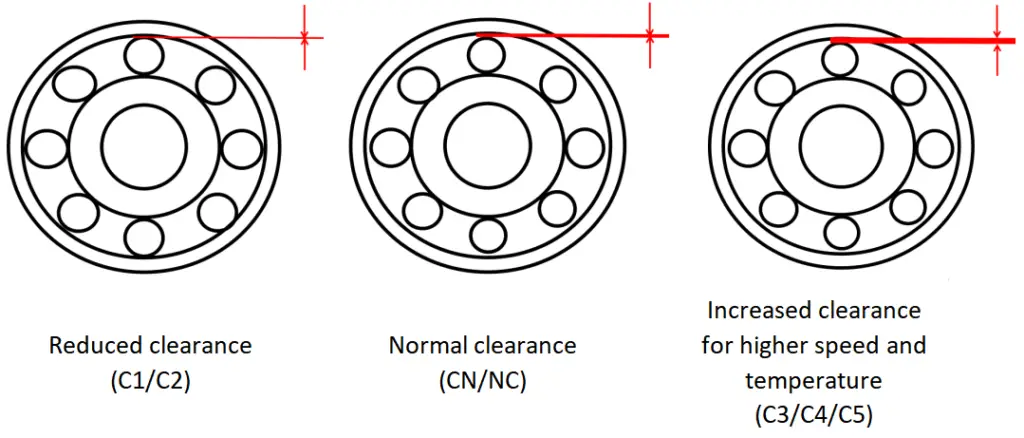
| Suffix | Clearance |
|---|---|
| C1 | Less than C2 |
| C2 | Less than normal |
| CN | Normal |
| C3 | Greater than normal |
| C4 | Greater than C3 |
| C5 | Greater than C4 |
Radial and Axial Loads:
- Radial Load: Forces acting perpendicular to the bearing’s axis.
- Axial Load: Forces acting parallel to the bearing’s axis.
Commonly Used Ball Bearings in Caster Wheels
We have created a list of the most popular sizes to make it quicker and easier for you to know the commonly used ball bearings in caster wheels.
| Bearing number | ID | OD | Width |
|---|---|---|---|
| 608 | 8 | 22 | 7 |
| 6001 | 12 | 28 | 8 |
| 6002 | 15 | 32 | 9 |
| 6003 | 17 | 35 | 10 |
| 6004 | 20 | 42 | 12 |
| 6005 | 25 | 47 | 12 |
| 6200 | 10 | 30 | 9 |
| 6201 | 12 | 32 | 10 |
| 6202 | 15 | 35 | 11 |
| 6203 | 17 | 40 | 12 |
| 6204 | 20 | 47 | 14 |
| 6205 | 47 | 52 | 15 |
How to Decode Ball Bearing Model Numbers
So, what do the codes on the ball bearing actually represent? Let’s break it down in more detail to understand their meaning.
Bearing codes generally consist of a “basic number,” and in some cases, additional prefix and suffix codes may be added at the beginning or end. These supplementary codes provide extra information about the bearing’s specific features, such as design modifications or protective sealing.
The basic number is the core part of the code and reveals essential details about the bearing, including its type, series number, and bore size.
To illustrate, let’s take a commonly used bearing as an example: (S) (6201) (ZZ). Here’s how each component of the code breaks down and what it signifies.

Prefix
Prefix codes on bearings are pretty rare, but you might run into one now and then. When they’re used, prefixes usually point out specific materials or design elements chosen by the manufacturer. For instance, in our example with a prefix of (S), it means the bearing is made of stainless steel. Here are a few other common examples to give you an idea.
| Prefix | Meaning |
|---|---|
| W | Stainless Steel (SKF brand) |
| S | Stainless Steel (FAG brand) |
First digit decoding
The first digit of the basic number identifies the type of bearing. In our example, the number (6) indicates that it is a single-row deep groove ball bearing.
| Bearing type code | Bearing name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Self-aligning Ball Bearing |
| 2 | Spherical Roller Bearing |
| 3 | Double Row Angular Contact Ball Bearing |
| 4 | Double Row Ball Bearing |
| 5 | Thrust Ball Bearing |
| 6 | Single Row Deep Groove Ball Bearing |
| 7 | Single Row Angular Contact Bearing |
| 8 | Felt Seal Bearing |
| and more… | … |
Second digit decoding
The second digit of the basic number indicates the bearing series and reflects its load capacity or toughness. In our example, the number (2) signifies its light toughness.
| Series code | Series code meaning |
|---|---|
| 0 | Extra Light |
| 1 | Extra Light Thrust |
| 2 | Light |
| 3 | Medium |
| 4 | Heavy |
| 8 | Extra Thin Section |
| 9 | Very Thin Section |
Third and fourth digit decoding
The third and fourth digits in the basic number represent the bore size, or the inner diameter (ID), of the bearing. In our example, the number 0 indicates that the bearing has a 12 mm bore size.
It’s important to note that for bore sizes of 20 mm and above, you typically time(x) the last two digits by 5 to determine the bore size. This rule applies to most standard types of bearings.
| Third and fourth digit | ID / Bore size(mm) |
|---|---|
| 00 | 10 |
| 01 | 12 |
| 02 | 15 |
| 03 | 17 |
| Starts from here, x5=ID | |
| 04 | 20 |
| 05 | 25 |
| 06 | 30 |
| and so on… | … |
Suffix
Suffixes indicate additional special features or design elements of a bearing, often relating to its sealing method. In our example, the suffix (ZZ) specifies that the bearing is shielded on both sides
| Suffix | Meaning of the suffix |
|---|---|
| Z | One side of the bearing is shielded |
| ZZ | Both sides of the bearing is shielded |
| RS | One side of the bearing is sealed |
| 2RS or DDU | Both sides of the bearing is sealed |
| C3 | Larger clearance |
| K | Taper bore |
| NR | Snap ring groove |
| M or MB | Machined brass cage |
Conclusion
Ball bearings reduce friction and enhance mobility, making caster wheels more efficient and durable. By exploring key terminology such as inner and outer diameters, seal types, and load capacities, you can gain a clearer understanding of the technical aspects of ball bearings. Familiarity with how ball bearing model numbers are decoded also helps clarify the specifications and design, making it easier to grasp their role in caster wheel functionality.
FAQs
-
Q: What type of bearing is in a caster wheel?
A: There are six commonly used bearing types for caster wheels: 1. plain bearing, 2. delrin bearing, 3. roller bearing, 4. sealed precision ball bearing, 5. tapered roller bearing, and 6. thrust ball bearing.
-
Q: Why are ball bearings better than roller bearings in caster wheel?
A: Ball bearings excel in supporting heavier loads and operating quietly, whereas roller bearings are more cost-effective but handle lighter loads and produce more noise.
-
Q: How do I know what size ball bearing I need?
A: Ball bearing sizes are determined by measuring three key dimensions: outer diameter (OD), bore size (ID), and width. These measurements are usually expressed in millimeters (mm). For accurate sizing, use a caliper or micrometer.
-
Q: Why are ball bearings used in wheels?
Ball bearings are rolling elements that utilize balls to keep the inner and outer moving parts separated. They convert kinetic friction into rolling friction, enhancing movement efficiency.
-
Q: How do ball bearings reduce friction?
A: Ball bearings decrease friction through the use of smooth, lubricated balls that effortlessly roll between the inner and outer surfaces. The core idea behind ball bearings is that rolling objects create less friction than sliding ones.
-
Q: What is the most common ball bearing in caster wheel?
A: The most widely used ball bearings in caster wheels are deep groove ball bearings. These bearings possess deep raceway grooves on both their inner and outer rings, which make them capable of handling both radial and axial loads.







