Caster wheels are essential yet often overlooked in our daily lives. From hospital beds gliding effortlessly across floors to industrial carts moving heavy machinery, these small yet mighty components simplify movement in countless ways. Did you know that over 75% of industrial equipment depends on caster wheels for mobility? Whether you’re here to pick the best caster wheel for your project or to learn how they work, you’re in the right place. Let’s roll into the details!
What are casters?
A caster (or castor) is a undriven assembly consisting of a wheel and a frame attached to the bottom of an object, allowing it to move easily by providing smooth, multidirectional mobility.

You’ll find them on everything from platform trolley and shopping carts to heavy-duty industrial machines. Unlike regular wheels, casters offer a unique advantage: they can swivel. This means they provide better mobility, especially in tight spaces. Whether you’re navigating a crowded store with a shopping cart or rolling an office chair across the room, casters make movement smooth and easy.
Difference Between Casters and Wheels
People often think that casters and wheels are the same, but there’s a fundamental difference between the two. A wheel is a simple round object that moves along a straight path. You see them on bicycles, cars, and other items where forward and backward movement is the goal.
Casters, on the other hand, are much more dynamic. They consist of not only a wheel but also a bracket or frame that allows the wheel to pivot. This gives casters their ability to swivel and move in any direction. This increased flexibility makes casters ideal for environments where objects need to move fluidly, like in warehouses, hospitals, and kitchens.
The History of Casters
Who Invented the Caster?
Casters, as we know them today, trace their origins to the 1870s when David A. Fisher filed a patent for the first industrial caster. His invention was designed to help ease the transportation of heavy machinery, making the lives of factory workers significantly easier. The concept revolutionized industries that required the frequent movement of bulky equipment.
Before the invention of casters, moving heavy objects required much more effort and manpower. With Fisher’s innovation, the process became more efficient, allowing businesses to increase productivity with less strain on workers.
Why Is It Called a ‘Caster’?
The term “caster” comes from the Latin word “castus,” which means “to throw” or “propel”. This is an apt name, as casters allow objects to be propelled smoothly from one place to another. Over time, the term has become synonymous with the entire assembly of a wheel and its bracket, which is designed to facilitate easy movement.
Caster vs. Castor: Clearing the Confusion
You may have seen both “caster” and “castor” used when referring to wheels, and it’s easy to get confused. In British English, “castor” is actually used to refer to what Americans call a “caster” wheel. So, while “caster” is the preferred term in the United States, “castor” can be the British term for the same wheel assembly. So, whether you’re reading British or American sources, both terms can refer to the same thing.
The Structure of a Caster
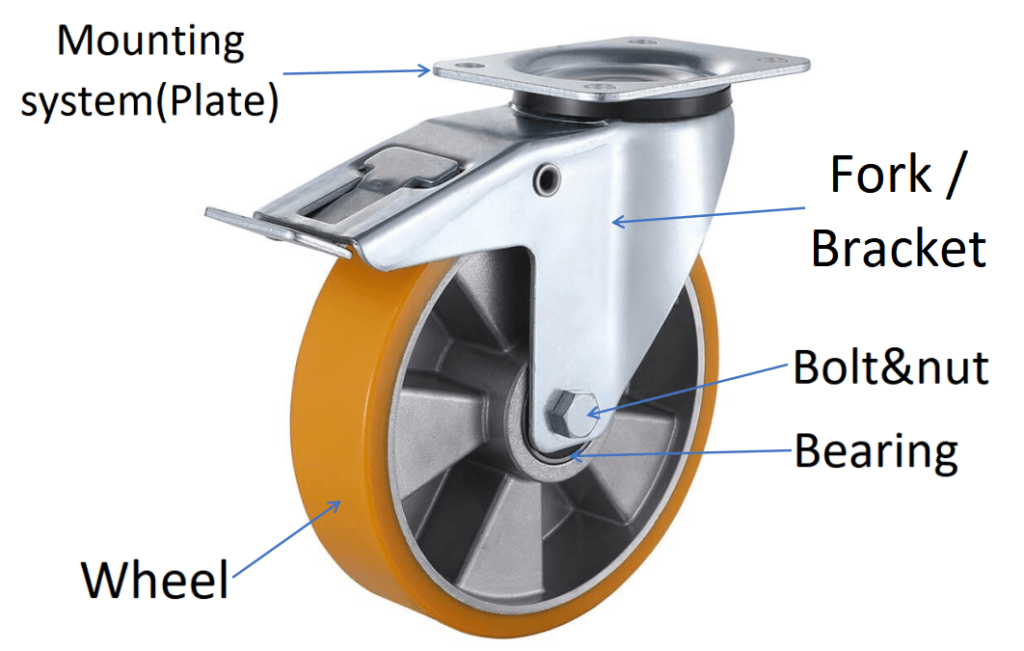
Casters may look simple, but each component plays a crucial role in how they function. Let’s break down the typical structure of a caster:
- Wheel: This can be made from materials like rubber, plastic, or polyurethane, depending on its intended use.
- Fork (or Bracket): The fork holds the wheel and attaches to the object. In swivel casters, the fork allows for full 360-degree rotation.
- Mounting System: Casters are attached to objects through plates or threaded stems. This mounting system ensures that the caster is securely fastened.
- Bearings: Many casters include bearings to reduce friction, making it easier for the wheel to rotate and roll smoothly.
- Axle nut and axle bolt: The axle nut secures the axle bolt in place, ensuring that the wheel stays attached to the frame and can rotate efficiently, while the axle bolt connects the wheel to the caster frame, providing a sturdy attachment point
To better understand how these components work together, here’s an image that illustrates the structure of a typical caster:
How Are Casters Made?
The manufacturing process of a caster varies based on its intended purpose. For example, casters used in industrial settings are typically made from durable materials like steel, while those used in home or office environments might be made from plastic or rubber. Here’s a general overview of how casters are made:

- Step1: Material Selection: Manufacturers choose materials like rubber, polyurethane, or metal based on the caster’s application and load requirements.
- Step 2: Molding and Casting: Depending on the material, wheels are either molded (for rubber, plastic, polyurethane, etc) or forged (for metal).
- Step 3: Stamping and forming: The steel parts of a caster including top plate, ballrace, and bracket, are usually made of hot rolled steel, through the process of cutting, blanking, stamping and forming, these components are ready for zinc plating.
- Step 4: Zinc plating: After the steel parts are finished, they will be sent for zinc plating, then they will be assembled into one complete piece.
- Step 5: Assembly: Adding the mounting system and attaching the wheel to the bracket, the complete caster is done.
- Step 6: Quality Control: Before casters are shipped out, we undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet performance standards, including load capacity and durability.
What Are Casters Used For?
No matter the industry, casters reduce the effort required to move objects, improving efficiency and safety.

Casters play an indispensable role in a wide range of applications, serving industries and everyday activities alike. From light-duty uses in homes and offices to heavy-duty industrial operations, casters have a place in nearly every corner of our lives. Below, we explore some of the most common and significant applications of casters in various environments.
1. Food process and service industry

Food service casters feature hygienic stainless steel designs, varying load capacities up to 2,500 lbs, quiet operation, and high durability to withstand harsh conditions. They are used in commercial kitchens, catering carts, food production facilities, and restaurants, enabling efficient and safe transport of equipment, ingredients, and dishes.
At WheelsWay, we provide caster solutions for the food service industry. Our casters enhance operational efficiency, safety, and durability, helping your business run seamlessly.
2. Entertainment and event industry

Casters in the entertainment industry enhance efficiency, safety, and flexibility. They are used on stage equipment, mobile stages, prop carts, AV equipment, and flight cases, allowing quick, quiet, and seamless movement. Durable and stable, casters enable easy transport and dynamic staging, ensuring smooth performances and safe handling of heavy and sensitive items.
At WheelsWay, we provide caster solutions for the entertainment and event industry. Our casters enhance operational efficiency, safety, and durability, helping your business run seamlessly.
3.Construction

Casters in the construction industry offer high load capacity and durability, enduring harsh conditions like chemicals and moisture. Their corrosion resistance ensures longevity outdoors. Designed for ease of movement, they facilitate transporting heavy materials, repositioning scaffolding, moving machinery, and organizing tool storage units, enhancing efficiency on job sites.
At WheelsWay, we provide caster solutions for the construction industry. Our casters enhance operational efficiency, safety, and durability, helping your business run seamlessly.
4. Medical and Healthcare Equipment

In hospitals and clinics, mobility is critical. From patient beds to medical carts, almost all movable equipment in a healthcare environment relies on casters. Casters are also found on stretchers, IV poles, medical equipment carts, and diagnostic machines, allowing for quick, efficient movement during emergencies or routine care.
At WheelsWay, we provide caster solutions for the medical and healthcare industry. Our casters enhance operational efficiency, safety, and durability, helping your business run seamlessly.
5. Industrial and Manufacturing Applications

Factories, warehouses, and construction sites use heavy-duty casters on machinery, pallets, toolboxes, and transportation trolleys to streamline operations. They are essential in automating material handling, reducing downtime, and enhancing overall workplace efficiency.
At WheelsWay, we provide caster solutions for the industrial and manufacturing industry. Our casters enhance operational efficiency, safety, and durability, helping your business run seamlessly.
6. Office Furniture and Equipment

One of the most visible uses of casters is in office settings. Chairs, desks, filing cabinets, and other pieces of office furniture often come equipped with casters, allowing for easy mobility within the workspace.
In addition to chairs, many office trolleys, printers, and computer servers are mounted on casters to facilitate easy movement around the office space.
7. Retail and Commercial Use

In the retail sector, casters are widely used in everything from shopping carts to display racks. Casters allow for easy rearrangement of store layouts and the quick transportation of goods from the stockroom to the sales floor. Even the heaviest display cases or shelves can be rolled into position without the need for lifting or disassembly.
8. Hospitality Industry

In hotels, restaurants, and event spaces, casters are widely used on a variety of equipment such as luggage carts, service trolleys, and banquet tables. These casters allow staff to transport luggage, food, beverages, and supplies easily and efficiently, ensuring smooth service delivery in hospitality settings.
9. Home and DIY Applications

Casters aren’t just limited to commercial and industrial uses, they also find a home in residential environments. You’ve likely encountered casters on rolling kitchen islands, under-bed storage units, laundry hampers, and even plant stands. These small but essential components help homeowners move items around with ease, making daily tasks more convenient.
10. Waste Management

Casters are essential in the waste management industry, where heavy containers and bins must be transported frequently. Trash bins, recycling containers, and industrial waste carts are equipped with casters to allow for smooth mobility.
How Do Casters Work?
Casters operate by reducing the friction between the object and the floor. When a force is applied—such as pushing a cart—the wheel rolls, allowing the object to move. The swivel design of many casters is what makes them so versatile, enabling them to rotate in any direction.
Let’s break down how they function in various situations:
- Attachment: Casters are usually attached via a plate or a stem. This secure attachment ensures the caster can bear the load it is intended to carry.
- Movement: When you push or pull an object with casters, the wheels rotate on their axle, allowing the object to roll. The swiveling feature helps you navigate tight spaces.
- Friction Reduction: Casters reduce the friction between the object and the ground, making it easier to move heavy items with minimal effort.
- Floor Protection: Certain casters are designed to protect floors from scratches, especially on delicate surfaces like hardwood. Soft rubber casters are ideal for such purposes.
- Design Variations: Casters come in a wide variety of designs, each suited to a particular use case. Some are built for speed, while others prioritize stability or load-bearing capacity.
- Load Distribution: Casters can ensure even weight spread, minimizing strain, and support an incredible range of weights, from lightweight chairs, industrial machinery, to containers.
Additionally, casters distribute the load across multiple wheels, preventing floor damage and making it easier to move heavier objects. Some casters even come equipped with brakes or locking mechanisms to provide added control.
Key Considerations When Choosing Caster Wheels
Choosing the right caster wheels might seem straightforward, but it involves a careful evaluation of your specific needs and the wheel’s features. Here’s a closer look at the key factors to consider:
- Load Capacity: Determine the maximum weight the wheels will need to carry. Heavy-duty caster wheels can support thousands of pounds, making them ideal for industrial equipment or heavy machinery. For lighter applications, such as office chairs or furniture, smaller load capacities are sufficient. Always opt for wheels rated higher than your heaviest load to ensure durability and safety.
- Surface Compatibility: The surface where the wheels will roll significantly affects performance. Rubber caster wheels work best on smooth indoor floors, providing quiet, non-marking movement. For rough or uneven surfaces, pneumatic wheels filled with air offer superior traction and shock absorption, making them ideal for outdoor use.
- Durability: Consider the material and design of the caster wheels to ensure longevity. Industrial settings often require robust materials like steel or reinforced polyurethane, while residential applications may prioritize quieter and less abrasive options. Regular maintenance, like cleaning and lubrication, also extends the wheels’ lifespan.
- Wheel size: The wheel material affects both durability and functionality. Rubber wheels are suitable for light-duty applications and protect delicate floors. Polyurethane wheels combine durability with floor protection, making them versatile. Metal or steel wheels, while durable, can damage certain surfaces and are best suited for heavy-duty or outdoor applications.
- Wheel material: The material of the wheel determines its functionality and performance. Rubber and polyurethane provide floor protection and quiet operation, making them ideal for indoor use. Steel and cast iron are more durable and suited for heavy-duty applications, while pneumatic wheels handle uneven surfaces with ease.
Understanding these factors ensures you select caster wheels suited to your specific needs. By investing in the right caster wheels and maintaining them properly, you’ll save time, effort, and money in the long run
Benefits of Caster Wheels
Whether for transporting goods, enhancing safety, or improving productivity, caster wheels are indispensable tools that simplify mobility and ensure long-term efficiency. It offers numerous advantages across various applications. Here’s a quick breakdown of their key benefits:
- Enhanced Efficiency
- Reduce friction and effort required to move objects.
- Save time and energy, especially for heavy loads in industrial and hospital settings.
- Versatility
- Available in various types, including swivel caster wheels for maneuverability and pneumatic caster wheels for outdoor terrain.
- Adaptable to a wide range of uses, from office furniture to industrial machinery.
- Improved Safety
- Locking mechanisms prevent unintended movement, ensuring stability.
- Ideal for applications like medical carts, ladders, and machinery where secure positioning is critical.
- Productivity Boost
- Ergonomic designs reduce physical strain, increasing worker efficiency.
- Studies show a 20% improvement in productivity in workplaces using caster wheels.
- Durability
- Designed to withstand heavy-duty usage and rough conditions, particularly in industrial settings.
Types of Casters
Casters are classified by various factors, including their load capacity, fitting style, and the specific purposes they serve.
By load capacity:

Light-duty casters:
Typically used for furniture, light carts, and small appliances.
Medium-duty casters:
Common in healthcare and retail for heavier carts and equipment.


Heavy-duty casters:
Found in industries like manufacturing, these casters can support the movement of heavy machinery and equipment.
Extra heavy-duty casters:
Engineered for extreme industrial applications, extra heavy-duty casters are built to carry exceptionally heavy loads, such as construction equipment or large shipping containers.

By mounting system:

Plate-mounted casters:
Attached to a flat, square or rectangular metal plate, featuring pre-drilled holes at each corner aligning with the mounting points on carts and other fixtures. Ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Stem-mounted casters:
Stem-mounted casters can fit into a socket or sleeve. Attached via a stem—a rod-like component—that anchors directly into furniture or equipment. Ideal for racks, tables, and various equipment.
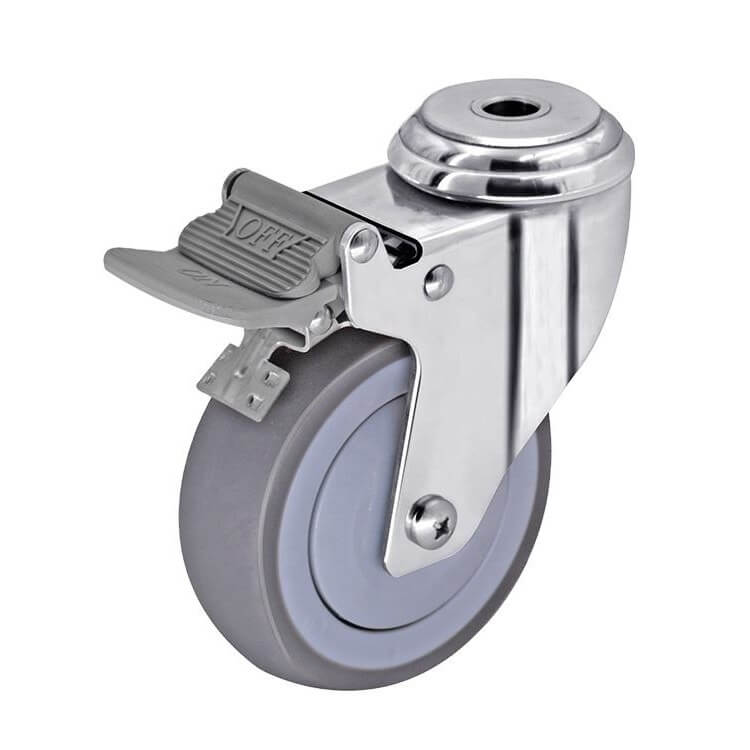
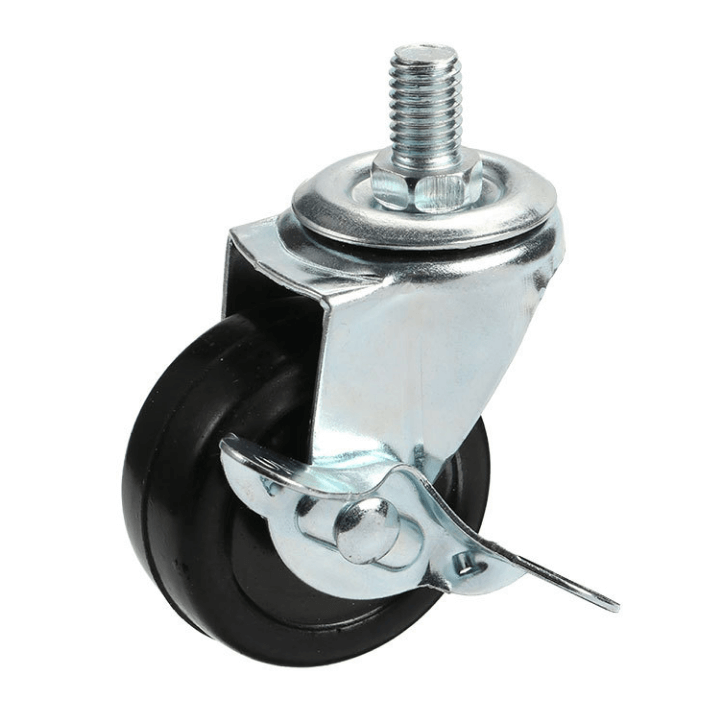

Bolt hole-mounted casters:
Bolt hole-mounted casters are featuring a single bolt hole at the top of the caster bracket, centered within the swivel head. This hole allows you to securely attach the caster to the equipment .
Corner fitting mounted:
Equipped with specialized brackets that attach directly to the corners of equipment or furniture, providing enhanced stability and support without the need to drill into flat surfaces. Ideal for applications where traditional mounting options are limited.

By specific purpose:
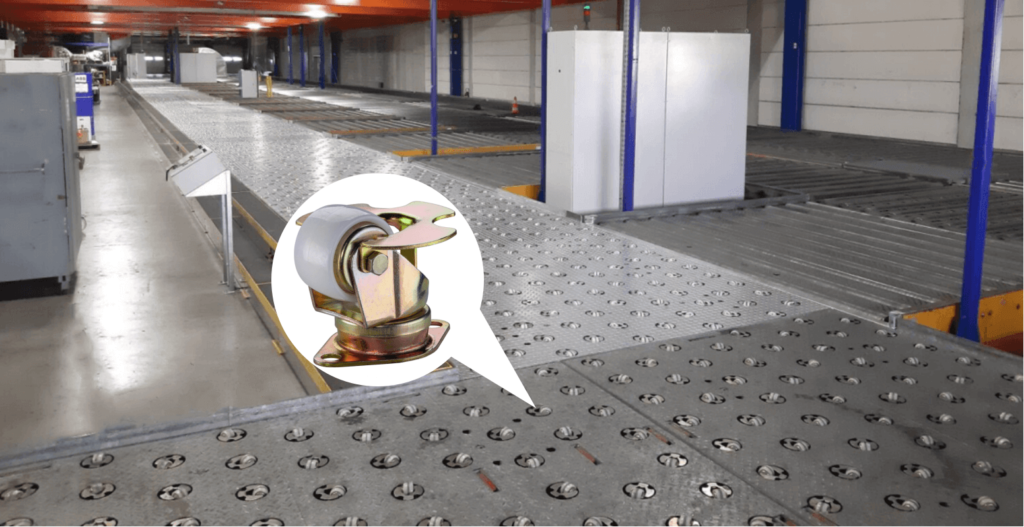
1. Air Cargo
Air cargo casters offer 360-degree rotation and dynamic movement, outperforming ball transfer units. These fully functional castors, integrated into floors or tables, provide fast, precise cargo guidance in any direction.

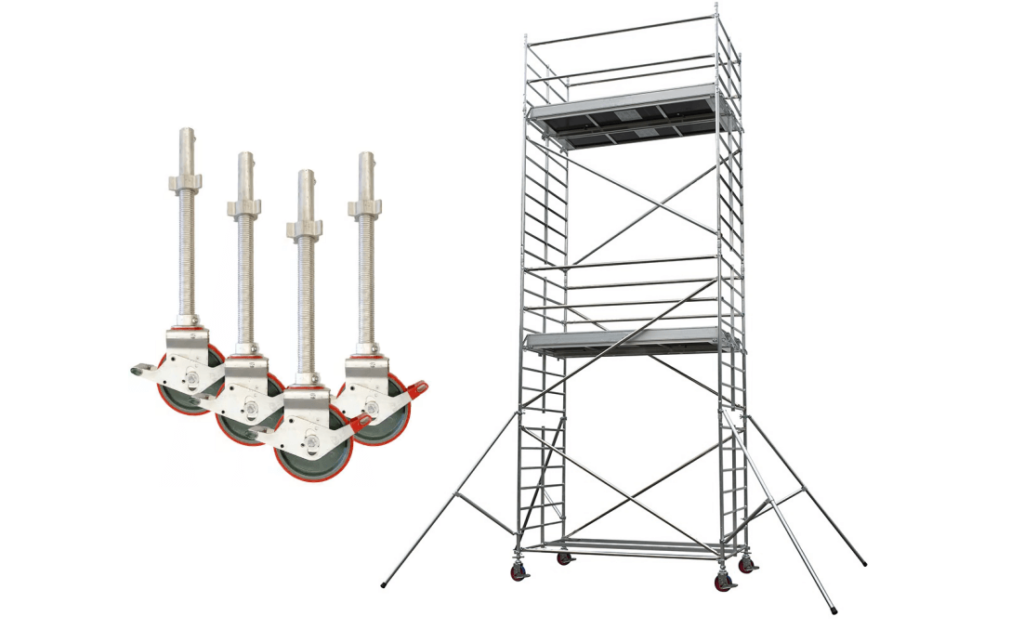
2. Mobile Scaffolding
A scaffolding caster features a stem mount and brake, allowing scaffolding units to be easily moved and securely locked in place for both mobility and stability.

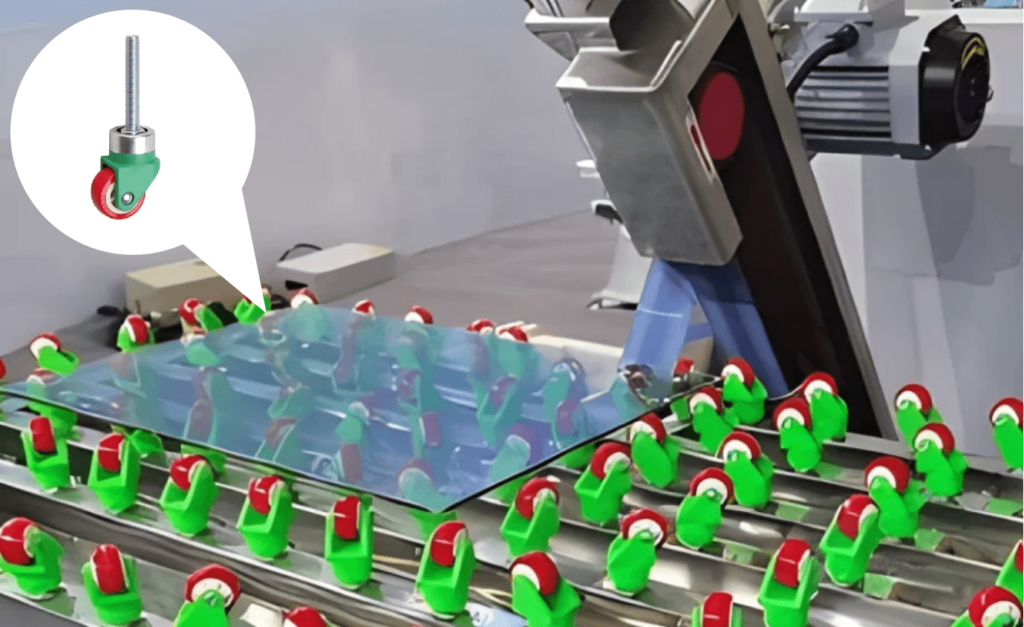
3. Glass Handling
Glass handling casters feature a debris-resistant raceway for smooth swiveling, with soft, non-marking wheels providing easy transport of glass sheets or other fragile items.
4. Escalator
An escalator caster is a non-powered wheel attached to carts or trolleys for use on escalators. It locks in place under load, ensuring stability and customer safety during transport.

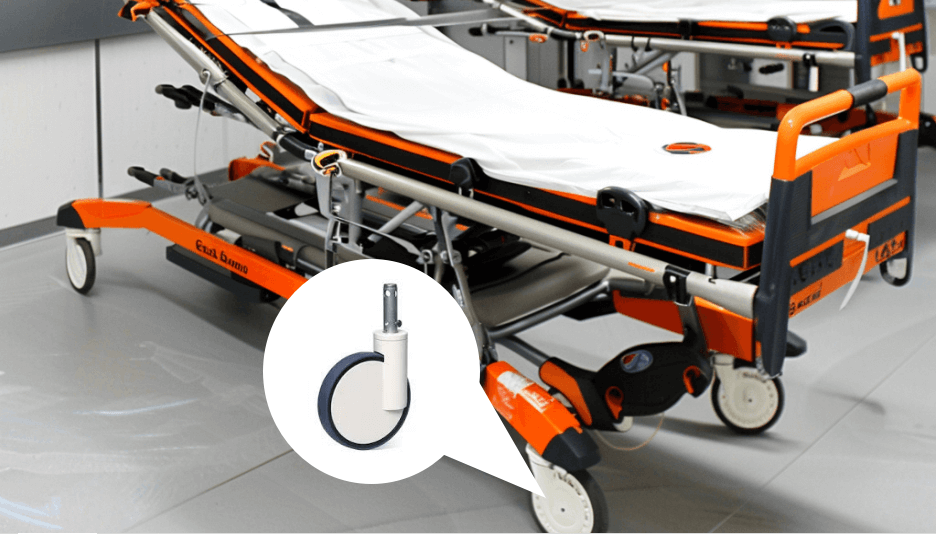
5. Medical Equipment
Medical casters are antimicrobial wheels used in hospitals to move equipment. Designed for reduced friction and noise, they enhance maneuverability with precision ball bearings for smooth, quiet transport.
6. Shipping Container Casters
Shipping container casters handle extreme loads, enabling easy movement and repositioning of large shipping containers in ports and warehouses.

7. Anti-Static and Conductive Casters

Conductive casters eliminate static by transferring current, instantly removing static electricity. Anti-static casters prevent generating over 250 volts during movement, reducing the risk of electrostatic hazards. Both casters protect sensitive electronics in environments like laboratories and clean rooms.
Caster Wheel Materials

Caster wheels are made from different materials based on the intended use and environment:
- Rubber: Soft and quiet, rubber wheels are perfect for protecting floors and providing smooth movement without noise.
- TPR (Thermoplastic Rubber): Combines the durability of plastic with the flexibility of rubber, offering smooth movement, good grip, and reduced floor damage, commonly used in indoor settings.
- TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer): Known for its flexibility and shock absorption, TPE wheels provide excellent wear resistance and are often used in environments requiring quieter and smoother mobility.
- Nylon(Polyamide): Strong and lightweight, polyamide (nylon) wheels offer high resistance to wear and chemicals, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications in harsh environments.
- PP(Polypropylene): Lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to chemicals, polypropylene wheels are commonly used for light to medium-duty applications where corrosion resistance is important.
- Polyurethane: Durable and resistant to chemicals, polyurethane wheels are often found in industrial settings, offering excellent load-bearing capacity and floor protection.
- Cast Iron: Extremely durable and capable of carrying heavy loads, cast iron wheels are used in rugged environments, but they can be rough on delicate surfaces.
- Foam Rubber: Soft and lightweight, foam rubber wheels provide excellent shock absorption and floor protection, making them ideal for transporting delicate or fragile items over uneven surfaces.
FAQs
Here are answers to some of the most common questions about caster wheels:
Q: How do I install caster wheels?
Most caster wheels are attached using screws or bolts. Some models come with threaded stems, while others use mounting plates. Ensure you align the wheel correctly and secure it tightly to prevent wobbling during use.
Q: What materials are best for caster wheels?
The material depends on your application. Rubber wheels are great for smooth indoor floors, while polyurethane offers a balance of durability and floor protection. Pneumatic wheels are ideal for rough outdoor terrain, and metal wheels suit heavy-duty industrial tasks.
Q: Are caster wheels suitable for outdoor use?
Yes, especially pneumatic caster wheels. These are designed to handle uneven and rugged surfaces, making them perfect for outdoor applications like construction sites or landscaping carts.
Q: How do I maintain my caster wheels?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning debris from the wheels, lubricating the swivel mechanism, and checking bolts for tightness. Replacing worn wheels ensures smooth and safe operation.
Q: Can caster wheels handle heavy loads?
Yes, industrial caster wheels are specifically designed to carry heavy loads, with some models supporting thousands of pounds. Always check the load capacity to match your specific requirements.
Q: Do caster wheels damage floors?
Not if you choose the right material. Rubber and polyurethane wheels are non-marking and protect delicate floors. Metal wheels, however, can scratch surfaces, so they’re better suited for industrial use.
Conclusion
Casters may seem like simple components, but they play an essential role in enabling smooth movement across a wide variety of settings, from industrial operations to household convenience. Their versatility and specialized designs allow them to meet the unique demands of different industries.
Understanding the different types of casters and their specific uses helps you select the right caster for your needs, ensuring efficiency, safety, and ease of movement. As these small yet powerful devices continue to evolve, they will undoubtedly remain critical components in industries around the world. If you got questions or a unique application in mind, contact us—we’re here to help!







