Step 1:Determine your product and mounting type



Plate-type swivel Plate-type fixed Bolt hole type



Screw-in type With expander With leveling mounts … and more
Click here to contact WheelsWay for more available items or OEM solutions!
Step 2 – Determine your Load Capacity.
Here’s the formula for calculating load capacity per caster:
Load per caster with safety factor = (total load × safety factor) / number of casters
“Total Load” is the equipment’s net weight plus its maximum additional load
“Safety Factor“ is an additional weight allowance added to the calculated load per caster to ensure that the casters can handle unexpected or temporary overloads, variations in load distribution, and wear & tear over time. It typically ranges from 1.0 to 3.0, although the specific value can vary depending on the application and industry standards.
- Safety factor: 1.0 to 1.5, for indoor manual transport, when the height of the obstacles is smaller than 5 % of the wheel diameter
- Safety factor: 1.5 to 2.2, for Outdoor manual transport, when the height of the obstacles is bigger than 5 % of the wheel diameter
- 1.4 to 2.0, for indoor power-driven transport, when the height of the obstacles is smaller than 5 % of the wheel diameter
- 2.0 to 3.0, for outdoor power-driven transport
Step 3 – Determine the size of the wheel
The bigger the wheel, the easier to push the caster forward, because it can roll over obstacles or rough and uneven surfaces more easily. This is because when the wheel is larger, obstacles look smaller compared to the wheel’s size, making it roll over them more smoothly.
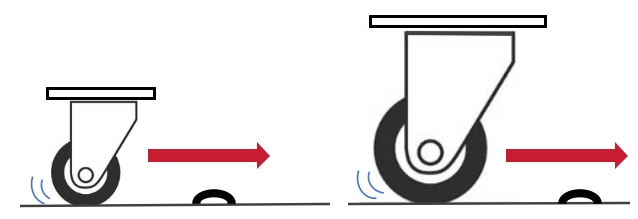
However, larger wheels will elevate the center of gravity, when you want to make sure things don’t tip over, especially if what you are carrying is heavy on top, smaller wheels are the better options. What’s more, smaller wheels can increase the force required to move, which will help the equipment to stay in place.
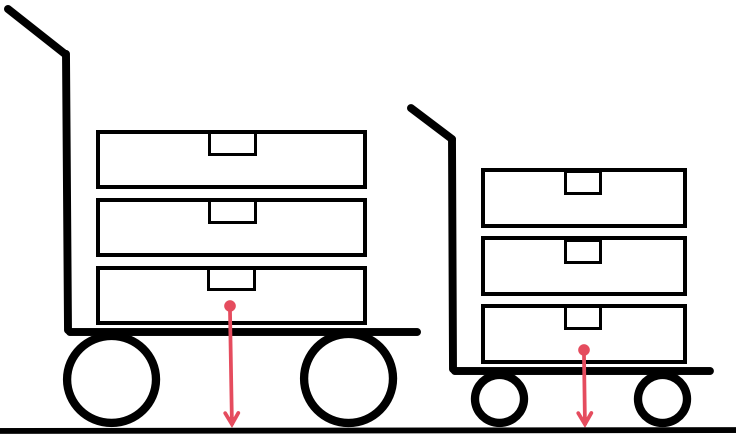
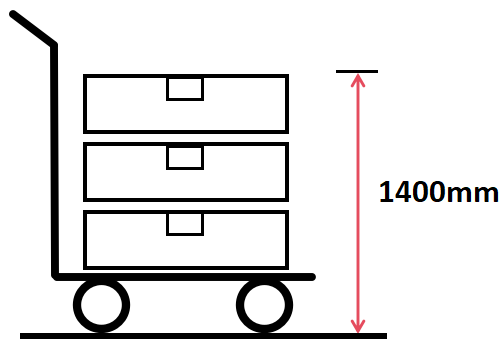
Another factor to consider is safety. It’s recommended that the total height of what you’re moving, including wheels and loaded goods, does not exceed 1400 mm. This will help to see better and avoid accidents.
Step 4 – Consider Your Application’s Environmental Influence
The following table describes the characteristics of some typical working environments that stage equipment casters often encounter.
| Application Environment | Environment Condition | Wheel Material Preferred | Noise Level Required | Cleaning | Corrosion Resistance necessity |
| Classrooms | Smooth, flat surfaces with occasional debris | Soft rubber, polyurethane, PVC | Low to minimize disruption during teaching | Casters should be easy to clean to remove dust and debris | Low |
| Library | Smooth, flat surfaces with occasional carpeted areas | Soft rubber, polyurethane, PVC | Very low to maintain a quiet environment for studying | Casters should be easy to clean to remove dust and debris, especially in carpeted areas | Low |
| Computer Labs | Smooth, flat surfaces with occasional cables | Polyurethane, rubber, Nylon | Moderate to low | Casters should be easy to clean to remove dust and debris | Low |
| Gymnasiums | Variable surfaces including hardwood floors, mats, and indoor sports courts. | Rubber, polyurethane, PVC | Moderate to low | Casters should be resistant to dirt, dust, and sweat commonly found in gym environments. | Moderate |
| Art rooms | Smooth, flat surfaces with occasional spills and splatters | Soft rubber, polyurethane, PVC | Moderate to low | Casters should be resistant to dirt, dust, and sweat commonly found in gym environments. | Moderate |
| Outdoor Learning Spaces | Variable outdoor surfaces including grass, gravel, and pavement | Pneumatic rubber, solid rubber, Nylon, plastic, polyurethane | Low | Casters should be resistant to dirt, dust, and sweat commonly found in gym environments. | High resistance to corrosion as outdoor environments are exposed to weather elements |
Step 5 – Select your Tread Material
Choosing the right material depends on several criteria, the table below shows the types and their main characteristics.
| Tread material | Maximum load | Performance on Uneven Floors | Resistance to Oil/Grease | Starting and Pulling Force | User Comfort | Shock/Vibration Absorption | Noise |
| Polyurethane | High | Good | Good | Low | Good | Good | Low |
| Elastic Rubber | Medium to high | Good | Good | Low | Good | Moderate | Moderate |
| Nylon | High | Fair | Excellent | Moderate | Fair | Poor | Low |
| Plastic | Medium to high | Fair | Fair | Low | Fair | Poor | Low |
| Pneumatic rubber | Medium | Excellent | Good | Good | Good | Good | Low |
| Thermoplastic Rubber | Medium | Good | Good | Low | Good | Good | Low |
Step 6 – Choose the bearing type
The wheel bearing is important for the rolling performance of a wheel and therefore for the mobility of the application equipment.
 Plain bearing
Plain bearing
The plain bearing is a simple and cost-effective wheel bearing, which is durable and free of maintenance under normal conditions. Plain bearings are mainly used for light-duty and low-speed applications. Since overheating can occur at high speeds under heavy loads, plain-bore cast iron wheels require regular lubrication.

Roller Bearing
The roller bearing is a sturdy, long-life grease lubricated, and maintenance-free wheel bearing type that consists of steel rollers(needles) fitted into a plastic or steel cage. These rollers roll between the axle tube and the wheel hub. As the wheel rotates around the axle, it has only rolling friction rather than sliding friction, resulting in low rolling resistance, even under heavy loads. In addition to the standard version, roller bearings are also available in stainless steel.
 Ball Bearing
Ball Bearing
A central ball bearing ensures precise, smooth running and effective sealing. it is integrated or injected directly into the wheel center. Two sealing caps are fitted as standard for added protection. Lubricated with long-life grease, these bearings are maintenance-free under regular conditions.